Understanding your customers is the cornerstone of business success. By gathering deep customer insights, businesses can unlock powerful opportunities for growth. Customer segmentation provides the key to these insights, enabling businesses to tailor their marketing efforts, improve product development, and drive sustainable growth. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the intricacies of customer segmentation, equipping you with the knowledge and tools to implement this powerful strategy in your business.
What Is Customer Segmentation?
Customer segmentation is the process of dividing a company’s customer base into distinct groups that share similar characteristics. Think of it like organizing a library: just as books are categorized by genre to help readers find what they’re looking for, customers are grouped by shared traits to help businesses serve them better.
Unlike customer profiling, which creates detailed portraits of individual customers, segmentation focuses on identifying patterns across groups of customers. This distinction is crucial because while profiling helps you understand individual customers deeply, segmentation enables you to make strategic decisions that impact larger groups efficiently.
At its core, customer segmentation is about recognizing that not all customers are the same. By identifying and understanding these differences, businesses can create more targeted and effective strategies across all areas of their operations.
Why Is Customer Segmentation Important?
The importance of customer segmentation can’t be overstated. Here are some key reasons why businesses should prioritize this strategy:
Personalized Marketing
By understanding the unique needs and preferences of different customer segments, businesses can create highly targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific groups.
Improved Product Development
Customer segmentation insights can inform product development, ensuring that new offerings meet the specific needs of target segments.
Enhanced Customer Experience
By tailoring their approach to different segments, businesses can provide a more personalized and satisfying customer experience.
Increased Customer Loyalty
When customers feel understood and valued, they’re more likely to remain loyal to a brand.
Efficient Resource Allocation
Segmentation allows businesses to focus their resources on the most valuable or promising customer groups.
Competitive Advantage
A deep understanding of customer segments can give businesses an edge over competitors who take a one-size-fits-all approach.
Customer Segmentation vs Market Segmentation
While often used interchangeably, customer segmentation and market segmentation are distinct concepts:
- Customer Segmentation focuses on dividing your existing customer base into groups based on shared characteristics.
- Market Segmentation is broader, encompassing both current customers and potential customers within the entire market.
Customer segmentation is more specific and actionable for businesses looking to optimize their current customer relationships and tailor their offerings to existing customers.
Types of Customer Segmentation
Customer segmentation can be approached in various ways, each offering unique insights into your customer base. Once you segment your customers, you’ll begin building customer personas. Let’s delve deeper into each type:
Demographic Segmentation
Divides customers based on attributes like age, gender, income, education, and occupation.
Example: A clothing retailer might segment customers by age and gender to tailor their product offerings and marketing messages.
Pros: Easy to implement, readily available data.
Cons: May oversimplify customer motivations.
Geographic Segmentation
Groups customers by location, such as country, region, city, or climate.
Example: A food delivery service might adjust its menu offerings based on regional culinary preferences.
Pros: Helps in localizing marketing efforts and product offerings.
Cons: May miss other important factors influencing customer behavior.
Psychographic Segmentation
Focuses on customers’ lifestyles, values, interests, and personalities.
Example: A luxury car brand might segment customers based on their values (e.g., status-seeking vs. environmentally conscious).
Pros: Provides deep insights into customer motivations.
Cons: Data can be challenging to collect and quantify.
Behavioral Segmentation
Categorizes customers based on their actions, such as purchasing habits, brand interactions, and product usage.
Example: An e-commerce platform might segment customers based on their browsing and purchasing history.
Pros: Directly relates to customer interactions with the brand.
Cons: Requires robust data collection and customer segmentation analysis capabilities.
Technographic Segmentation
Groups customers based on their technology adoption and usage patterns.
Example: A software company might segment customers based on the types of devices or operating systems they use.
Pros: Particularly useful for tech-related products or services.
Cons: May become quickly outdated due to rapid technological changes.
Needs-Based Segmentation
Divides customers according to their specific needs or pain points.
Example: A healthcare provider might segment patients based on their specific health concerns or treatment needs.
Pros: Directly addresses customer pain points.
Cons: Needs can change over time, requiring frequent reassessment.
Value-Based Segmentation
Segments customers based on their economic value to the business.
Example: A subscription service might segment customers based on their lifetime value or subscription tier.
Pros: Helps in prioritizing resources towards high-value customers.
Cons: May lead to neglect of potentially valuable customer groups.
Types of Customer Segmentation
| Type | Description | Pros | Cons |
| Demographic | Divides customers based on attributes like age, gender, income, education, and occupation. |
| May oversimplify customer motivations |
| Geographic | Groups customers by location, such as country, region, city, or climate. | Helps in localizing marketing efforts and product offerings | May miss other important factors influencing customer behavior |
| Psychographic | Focuses on customers’ lifestyles, values, interests, and personalities. | Provides deep insights into customer motivations | Data can be challenging to collect and quantify |
| Behavioral | Categorizes customers based on their actions, such as purchasing habits, brand interactions, and product usage. | Directly relates to customer interactions with the brand | Requires robust data collection and analysis capabilities |
| Technographic | Groups customers based on their technology adoption and usage patterns. | Particularly useful for tech-related products or services | May become quickly outdated due to rapid technological changes |
| Needs-Based | Divides customers according to their specific needs or pain points. | Directly addresses customer pain points | Needs can change over time, requiring frequent reassessment |
| Value-Based | Segment customers based on their economic value to the business. | Helps in prioritizing resources towards high-value customers | May lead to neglect of potentially valuable customer groups |
How to Conduct Customer Segmentation in 5 Steps
Now that we understand the importance and types of customer segmentation, let’s explore how to implement it effectively:
1. Define Your Objectives
Start by clearly outlining what you hope to achieve through customer segmentation. Are you looking to improve marketing effectiveness, develop new products, or enhance customer retention? Your objectives will guide the entire segmentation process.
2. Gather and Analyze Data
Collect relevant data about your customers. This may include:
- Demographic information
- Purchase history
- Website behavior
- Survey responses
- Customer service interactions
Tools like Prelaunch can be invaluable in this step, offering robust customer insights and segmentation capabilities.
3. Identify Segmentation Criteria
Based on your objectives and the data collected, determine which criteria you’ll use to segment your customers. This could be a combination of demographic, behavioral, and psychographic factors.
4. Create and Analyze Segments
Use your chosen criteria to divide your customer base into distinct segments. Analyze each segment to understand its unique characteristics, needs, and behaviors.
Prelaunch’s customer segmentation feature can streamline this process, allowing you to easily create and visualize your customer segments. The platform bases each segment on real data from surveys, interviews, and confirmed purchase intent.
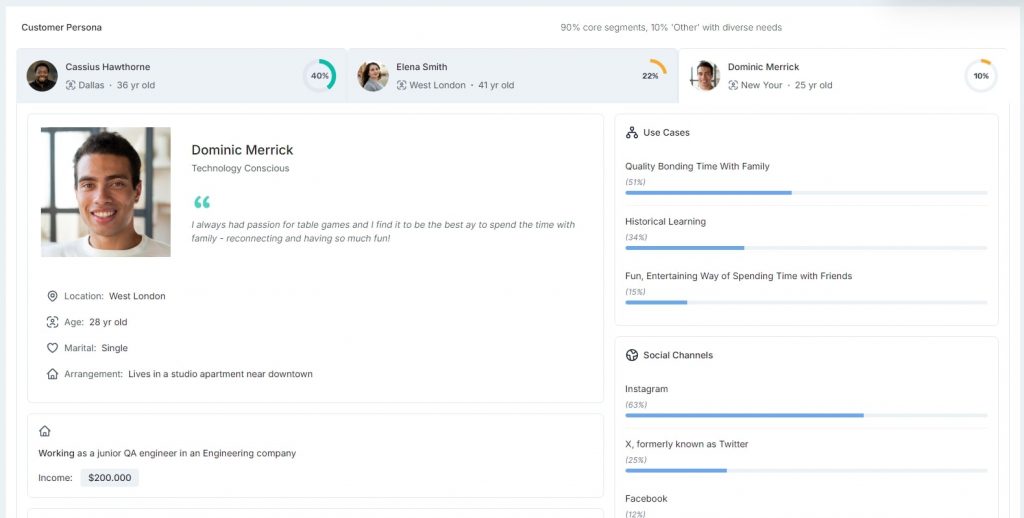
5. Implement and Iterate
Apply your segmentation insights to your marketing, product development, and customer service strategies. Continuously monitor the performance of your segments and refine your approach as needed.
Customer Segmentation Examples
Let’s explore some real-world customer segmentation models that have proven to be very effective:
Spotify

Segmentation Type: Behavioral
Approach: Spotify uses listening history and habits to create personalized playlists and recommendations.
Impact: Increased user engagement and subscription retention.
Nike

Segmentation Type: Psychographic and Demographic
Approach: Segments customers based on athletic interests and demographic factors.
Impact: Tailored product lines and marketing campaigns for different athlete types.
Starbucks

Segmentation Type: Geographic and Behavioral
Approach: Customizes menu offerings based on local preferences and tracks individual purchase history.
Impact: Localized product offerings and personalized rewards program.
Dollar Shave Club

Segmentation Type: Value-based and Demographic
Approach: Segments customers based on subscription tier and grooming needs.
Impact: Customized product bundles and targeted upselling strategies.
Customer Segmentation Tools
While manual segmentation is possible, using specialized tools can greatly enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of your efforts. Here are some popular customer segmentation tools:
Prelaunch
Offers powerful customer insights and segmentation capabilities, ideal for businesses looking to validate and launch new products. Combines segmentation with product validation, allowing businesses to test ideas with specific customer groups before full launch.
Best for: Enterprises and established businesses launching new products or entering new markets. (It can also prove to be a great springboard for startups as well in their strategic planing.)
Provides robust CRM and marketing automation capabilities with built-in segmentation tools. Integrates segmentation across marketing, sales, and service platforms.
Best For: Businesses looking for an all-in-one marketing and sales solution.
Offers email marketing segmentation features for targeted campaigns. User-friendly interface with pre-built segmentation options.
Best For: Small to medium-sized businesses focusing on email marketing.
Provides website visitor segmentation based on various behavioral and demographic factors. Deep integration with web analytics and Google’s advertising ecosystem.
Best For: Businesses looking to segment website visitors and online customers.
Offers advanced CRM segmentation capabilities for sales and marketing teams. Highly customizable with a vast ecosystem of integrations.
Best For: Large enterprises with complex segmentation needs.
Conclusion
Customer segmentation is a powerful strategy that can transform your business approach. By understanding and implementing various types of segmentation and following a structured process, businesses can gain valuable insights into their customer base and tailor their efforts accordingly. With tools like Prelaunch at your disposal, implementing a robust customer segmentation strategy has never been easier, enabling you to drive sustainable business growth and stay ahead of the competition.
FAQs
What are the 5 key customer segments?
While customer segments can vary widely depending on the business and industry, five common types of customer segments are:
- High-Value Customers
- Loyal Customers
- Potential Churners
- New Customers
- Lost Customers
What is the difference between customer segmentation and customer personas?
Customer segmentation divides your entire customer base into groups with shared characteristics. Customer personas, on the other hand, are fictional representations of ideal customers within each segment. While segmentation provides a broad view of your customer groups, personas offer a more detailed, narrative-driven profile of representative customers within those groups.
How can customer segmentation help with product development?
Customer segmentation can significantly enhance product development by:
- Identifying unmet needs within specific customer groups
- Prioritizing features based on segment preferences
- Tailoring products to the specific requirements of high-value segments
- Informing pricing strategies based on segment willingness to pay
- Guiding the development of complementary products or services for different segments
By aligning product development with the needs and preferences of specific customer segments, businesses can create more targeted, successful products and increase their overall market impact.



