In the fast-paced world of product development, prototype testing is a crucial step that can make or break your success. By validating your creations with real users before full-scale production, you can save time, money, and resources while ensuring your product meets market needs. This article will guide you through the essentials of prototype testing, its importance, methods, and best practices to help you launch your product with confidence.
Why is Testing and Evaluating a Prototype Important?
Prototype testing is the process of evaluating an early version of a product with target users to validate concepts, functionalities, and design decisions before final development. It involves creating a prototype—a preliminary model of your product—and gathering user feedback to identify potential issues, improve usability, and ensure the product meets user needs and expectations.
Why Is Prototype Testing Important?
Prototype testing plays a crucial role in the product development process, offering numerous benefits that can significantly impact your product’s success. Let’s explore the key reasons why prototype testing is essential:
Early Problem Detection
One of the primary advantages of prototype testing is the ability to identify and address issues early in the development process. By catching problems at the prototype stage, you can save substantial time and resources that would otherwise be spent on fixing issues in later stages. Additionally, this early detection prevents major design flaws from making their way into the final product, reducing the risk of costly recalls or extensive post-launch modifications.
User-Centric Design
Prototype testing involves giving your product to real users, which allows you to gain valuable insights into their preferences, behaviors, and pain points. It helps you validate assumptions about user needs and expectations, enabling you to refine your product to better align with user requirements, thereby increasing its chances of market success.
Risk Mitigation
Testing your prototype with target users allows you to reduce the likelihood of market failure by validating your concept before full-scale production. It helps identify potential barriers to adoption or usage and provides insights into initial user reactions, enabling you to adjust your strategy accordingly.
Cost-Effectiveness
Making changes during the prototype phase is significantly more cost-effective than modifying a finished product. Prototype testing helps you avoid expensive redesigns or feature overhauls post-launch, allocate resources more efficiently by focusing on features and improvements that matter most to users, and reduce overall development costs by streamlining the product creation process.
Informed Decision-Making
The data gathered from prototype testing empowers you to make evidence-based decisions about design and development choices, prioritize features and improvements based on user feedback, and allocate resources more effectively by focusing on areas that will have the most significant impact.
Stakeholder Communication
Prototypes serve as powerful communication tools by effectively conveying your ideas to team members, investors, and other stakeholders. They demonstrate the product’s potential and help gather support for your vision while aligning all parties involved in the project through a tangible representation of the product.
Prototype Testing Methods
Prototype testing encompasses a wide range of methods, each suited to different stages of product development and specific testing objectives. Let’s explore some of the most effective prototype testing methods:
Low-Fidelity Methods
Sketches and Diagrams
Sketches and diagrams are quick, low-fidelity visualizations ideal for early-stage concept testing. They allow you to:
- Gather initial feedback on overall direction and feasibility
- Rapidly iterate on ideas without significant time or resource investment
- Communicate basic concepts and layouts to stakeholders
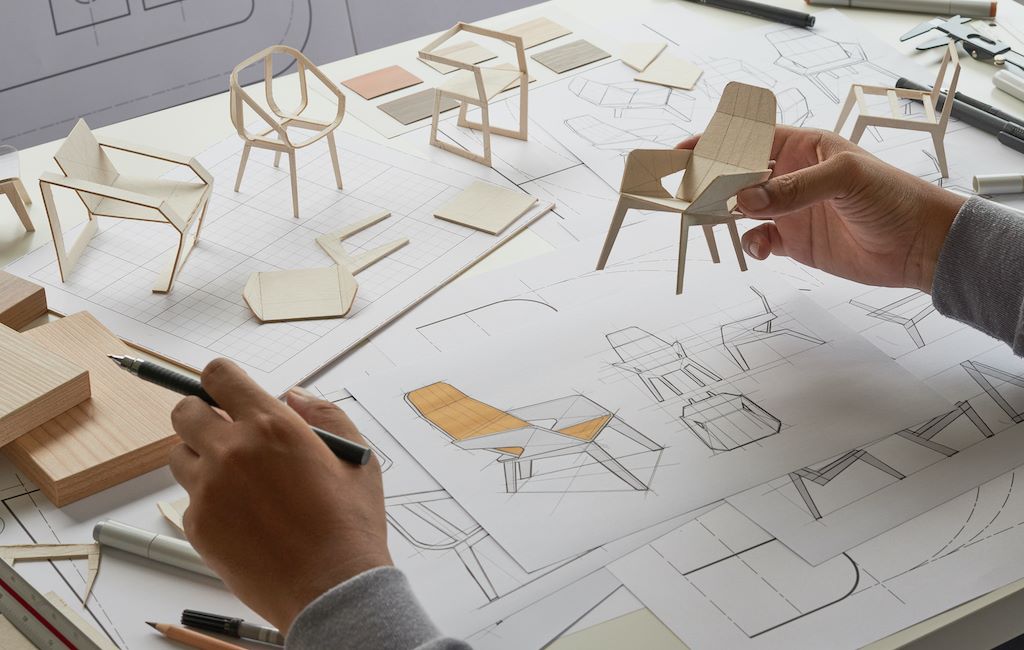

Paper Prototypes
Paper prototypes involve creating physical, interactive representations of your product using paper, cardboard, or other simple materials. This method:
- Enables quick and inexpensive testing of user interfaces and interactions
- Encourages creativity and collaboration within your team
- Allows for easy modifications during testing sessions
Medium-Fidelity Methods
Wireframes
Wireframes are digital layouts that focus on information architecture and user flow. They help you:
- Test the structural elements of your design without the distraction of visual details
- Validate navigation and content organization
- Identify potential usability issues early in the design process
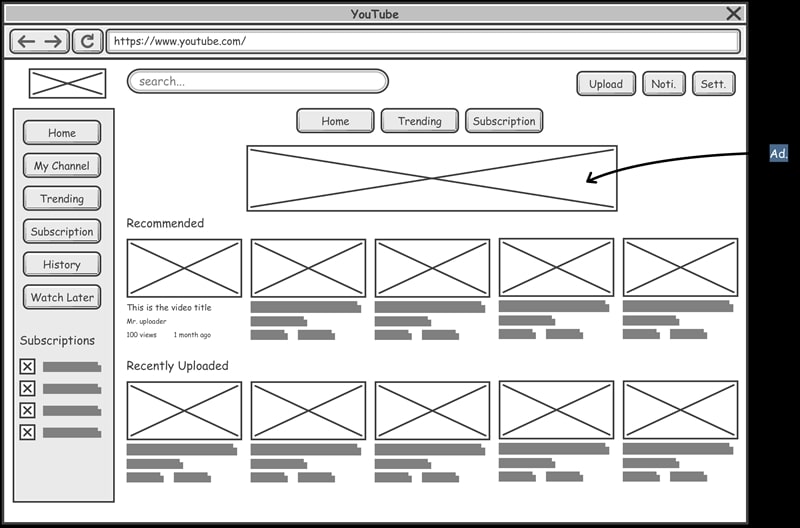
Interactive Prototypes
Interactive prototypes are clickable digital models that simulate user interactions. These prototypes:
- Help identify usability issues and areas for improvement in navigation and functionality
- Provide a more realistic user experience compared to static designs
- Allow for testing of complex interactions and user flows

High-Fidelity Methods
3D Printing or Rapid Modeling
For physical products, 3D printing or rapid modeling creates tangible prototypes that allow you to:
- Gather feedback on aesthetics and perceived quality
- Test form, fit, and basic functionality
- Evaluate ergonomics and user interaction with the physical product
Functional Prototypes
Functional prototypes are working models that closely resemble the final product in both form and function. They enable you to:
- Conduct comprehensive usability testing
- Evaluate the product’s performance under real-world conditions
- Identify any final adjustments needed before full-scale production
Specialized Methods
Role-Playing and Experiential Prototyping
This method involves simulating real-world scenarios to explore user experiences and emotional responses. It helps you:
Gather qualitative insights that may not be apparent through other testing methods
Understand how users might interact with your product in various contexts
Identify potential pain points or opportunities for improvement in the user journey
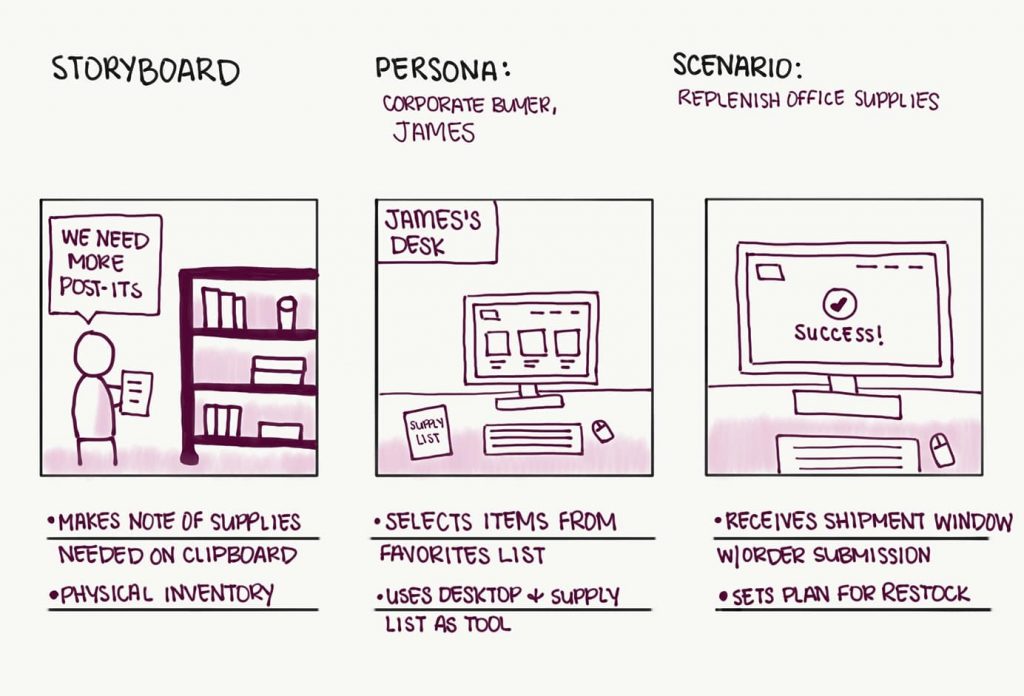
Storyboarding
Storyboarding involves creating visual narratives to illustrate user journeys and product use cases. This method:
- Facilitates communication of complex scenarios to stakeholders and team members
- Helps teams align on the overall user experience and product vision
- Identifies potential gaps or inconsistencies in the user journey
How to Test a Prototype
Conducting effective prototype testing requires careful planning and execution. Of course, you’ll be one major step ahead of the game if you go through the prelaunch process first. Why? Because concept validation platforms like Prelaunch allows you to make sure your prototype is as close to the real thing as can be by leveraging feedback from your future customers who’ve confirmed their purchase intent. Translated: They tell you what kind of product they need, so you can create a product they need.
For how to test a prototype, follow these steps to ensure you get the most valuable insights from your testing process:
1. Define Clear Objectives
Before beginning your prototype testing, it’s crucial to establish clear goals and objectives. Ask yourself:
- What specific aspects of the product do you want to validate?
- Are you testing functionality, usability, aesthetics, or a combination of these?
- What key questions do you need answered to move forward with confidence?
By defining your objectives upfront, you’ll be able to design more focused and effective tests.
2. Choose the Right Prototype
Select a prototyping method that aligns with your testing goals and stage of development. Consider:
- The fidelity level required to test your objectives effectively
- The resources and time available for creating the prototype
- The type of feedback you need at this stage of development
Remember, different stages of your project may require different types of prototypes.
3. Identify Your Target Users
Recruiting the right participants is crucial for gathering relevant feedback. To do this effectively:
- Create detailed user personas to guide your recruitment process
- Seek participants who closely match your target audience demographics and behaviors
- Consider using a mix of existing customers and potential new users for a well-rounded perspective
4. Create a Comprehensive Test Plan
Develop a structured test plan that outlines:
- Specific tasks for participants to complete
- Questions to ask during and after the testing session
- Metrics you’ll use to measure success (e.g., task completion time, error rates, satisfaction scores)
- The overall flow of the testing session
A well-designed test plan ensures consistency across sessions and helps you gather comparable data.
5. Conduct the Test
When running your prototype testing sessions:
- Create a comfortable, neutral environment for participants
- Clearly explain the purpose of the test and set expectations
- Encourage participants to think aloud as they interact with the prototype
- Observe and take detailed notes on user behavior and comments
- Ask follow-up questions to clarify observations and gather deeper insights
6. Analyze Results
After completing your testing sessions:
- Review all data collected, including notes, recordings, and any quantitative metrics
- Look for patterns and common themes across different users
- Identify both positive aspects and areas for improvement
- Prioritize issues based on their impact on the user experience and your business goals
7. Iterate and Refine
Use the insights gathered from your analysis to:
- Make informed changes to your product design
- Address identified issues and pain points
- Enhance features that resonated positively with users
- Develop new ideas based on user feedback and observations
8. Repeat as Necessary
Prototype testing is an iterative process. Plan for multiple rounds of testing as your product evolves:
- Conduct follow-up tests to validate changes made based on initial feedback
- Test new features or design iterations as they are developed
- Consider A/B testing for alternative solutions to identified problems
Remember, each round of testing brings you closer to a product that truly meets user needs and expectations.
Best Prototype Testing Tools
Choosing the right tools can significantly enhance your prototype testing process. Here’s an in-depth look at some of the best prototype testing tools available:
InVision
InVision is a comprehensive digital product design platform that excels in creating interactive prototypes.
Key features:
- Seamless integration with design tools like Sketch and Photoshop
- Real-time collaboration features for team feedback
- Built-in user testing capabilities
- Workflow management tools
Best for: UX/UI designers, product managers, and design teams working on digital products.
Balsamiq
Balsamiq is renowned for its simplicity in creating low-fidelity wireframes quickly.
Key features:
- Drag-and-drop interface for rapid prototyping
- Large library of UI elements and icons
- Easy sharing and collaboration options
- Support for both web and desktop applications
Best for: Early-stage concept testing, UX designers, and product managers needing quick mockups.
Proto.io
Proto.io offers a powerful platform for creating high-fidelity, interactive prototypes for web and mobile applications.
Key features:
- No coding required for creating complex interactions
- Extensive library of UI components and templates
- Integration with user testing tools
- Support for animations and micro-interactions
Best for: Designers and product teams needing detailed, interactive prototypes for comprehensive testing.
Userbrain
Userbrain specializes in remote user testing, allowing you to gather video feedback from real users.
Key features:
- Access to a diverse pool of testers
- Quick turnaround times for feedback (often within hours)
- Customizable test scenarios and questions
- Detailed analytics and reporting features
Best for: Teams needing quick, unmoderated user testing for websites and digital products.
Principle
Principle is designed for creating animated and interactive user interface designs for various platforms.
Key features:
- Advanced animation capabilities
- Support for complex user flows and interactions
- Easy integration with design tools like Sketch
- Export options for different platforms (iOS, Android, web)
Best for: UI designers focusing on creating dynamic, animated prototypes.
Additional Tools to Consider
- Figma: A collaborative interface design tool with robust prototyping features.
- Adobe XD: Part of the Adobe Creative Suite, offering powerful design and prototyping capabilities.
- Axure RP: Ideal for creating highly functional, interactive prototypes with conditional logic.
- Marvel: A user-friendly platform for creating both low and high-fidelity prototypes.
When choosing a tool, consider factors such as:
- Collaboration features and team size
- Your team’s skill level and familiarity with different tools
- The complexity of prototypes you need to create
- Integration with your existing design and development workflows
- Budget and pricing models
Successful Prototype Testing Examples
Loliware’s Edible Cups
Loliware, founded by Chelsea Briganti and Leigh Ann Tucker, showcases the power of iterative prototype testing. Their journey to create biodegradable, edible drinking cups demonstrates how persistence and user feedback can lead to product success:
- Initial Concept: Eco-friendly, biodegradable cups to replace plastic waste.
- First Prototype: Used gelatin, but testing revealed poor taste and smell.
- Iteration: Switched to agar, improving taste, smell, and vegan-friendliness.
- Validation: Won a design competition, garnering attention and initial orders.
- Market Success: Secured funding and large orders, launching a successful product.
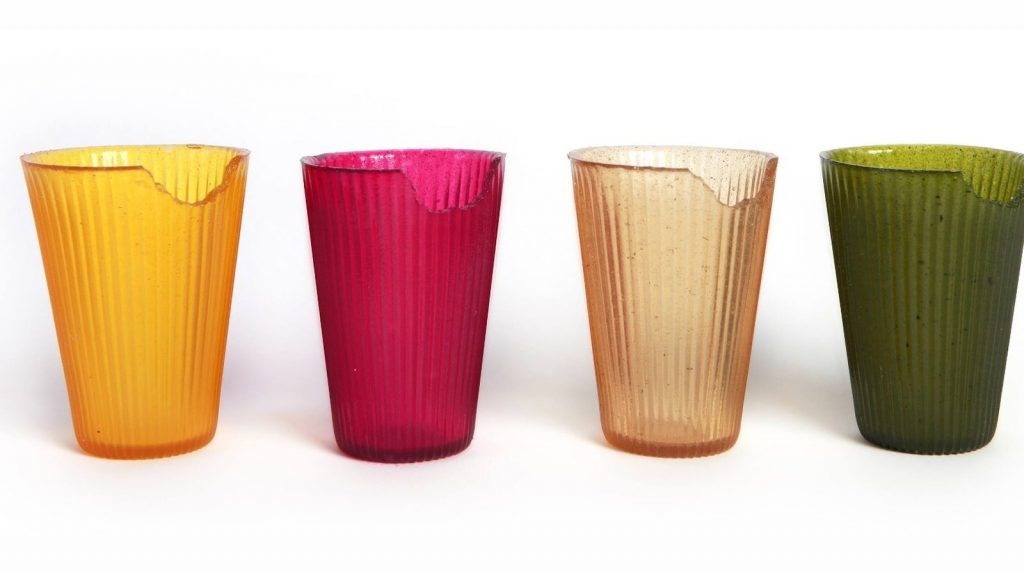

This example illustrates how prototype testing can help refine a product, overcome challenges, and ultimately lead to market success.
Dyson’s Cyclone Vacuum Cleaner
James Dyson’s development of the cyclone vacuum cleaner demonstrates the importance of persistent prototype testing:
- Outcome: Revolutionized the vacuum cleaner industry with a bagless, high-suction product.
- Initial Problem: Conventional vacuum bags lost suction as they filled with dust.
- Prototype Approach: Built over 5,000 prototypes over 15 years.
- Testing Method: Each prototype was rigorously tested for suction efficiency and durability.
- Key Iteration: Discovered the cyclone technology principle after observing industrial sawmills.
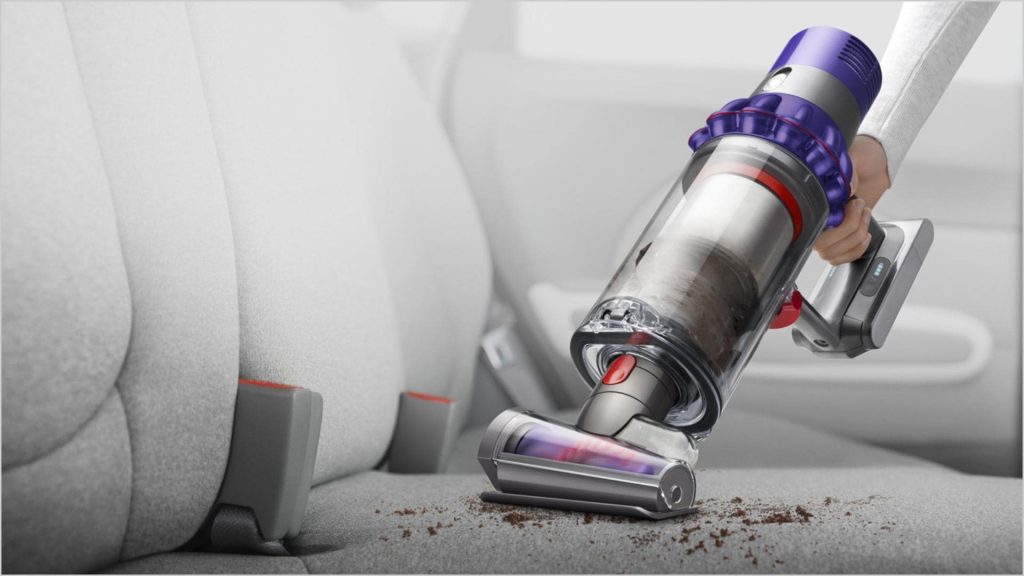

This example shows how extensive prototype testing, even over a long period, can lead to groundbreaking product innovations.
Tesla’s Model S Battery Pack
Tesla’s development of the Model S electric car battery pack highlights the importance of prototype testing for complex systems:
- Result: Produced an innovative battery pack design that set new standards for electric vehicle range and safety.
- Initial Challenge: Creating a safe, efficient, and long-range battery pack for electric vehicles.
- Prototype Design: Developed a unique “skateboard” chassis with integrated battery pack.
- Testing Method: Conducted extensive crash tests, thermal management tests, and real-world driving simulations.
- Key Discovery: Identified the need for a complex cooling system to maintain optimal battery temperature.
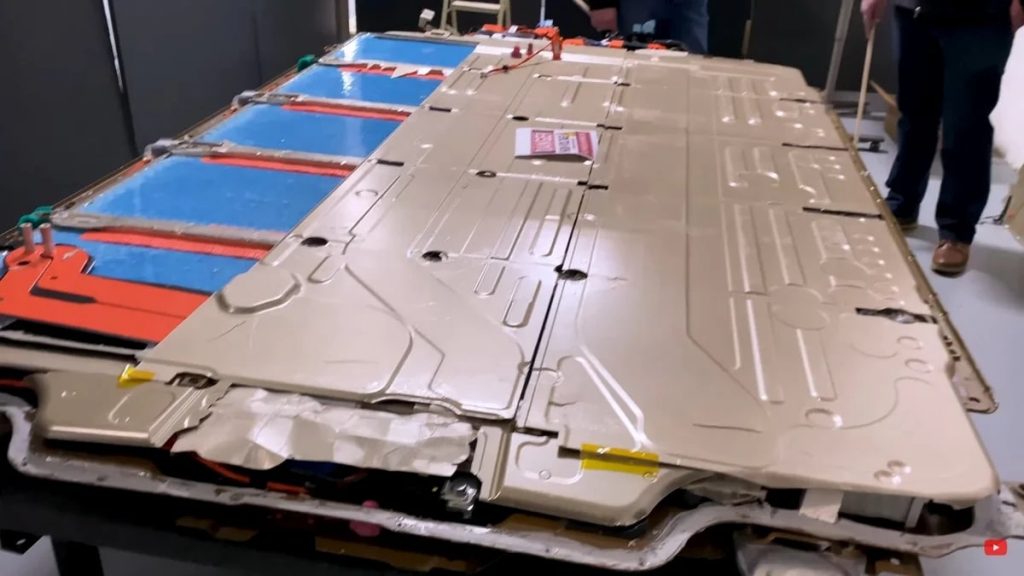

This example demonstrates how thorough prototype testing can lead to breakthroughs in product performance and safety, especially in high-stakes industries.
Conclusion
Prototype testing is an invaluable step in product development. By embracing this approach, you can create products that truly resonate with your target audience, minimize risks, and increase your chances of market success. Remember, the key to effective prototype testing lies in iteration, user feedback, and a willingness to adapt based on insights gained. So, don’t skip this crucial phase—test early, test often, and launch with confidence




